Ammonia refrigeration working principle
 |
| Industrial refrigeration basics |
Basic principles of the industrial refrigeration system - Ammonia refrigerant. In this video we will look at the basics of industrial refrigeration systems with a focus on ammonia refrigeration systems, we will start with the basics and progress to cover some typical systems for single stage systems, two stage systems and cascaded systems. to help you learn the basics of industrial refrigeration.
Watch the YouTube tutorial at the end of the article.
Do you want a free industrial refrigeration course? Start your free online ammonia courses today by clicking here
Danfoss Learning is an online training platform that offers hundreds of free online courses that you can access from your computer, smartphone or tablet. Find out how ammonia can help make industrial refrigeration applications more efficient and environmentally friendly with our eLesson series today.
🏆 Start learning now at http://bit.ly/StartAmmoniaeLesson
Where are industrial refrigeration systems located?
Industrial refrigeration applications are typically used in places like cold food storage, dairy processing, beverage production, ice skating rinks, and heavy industry, those kinds of places. These are full-scale cooling systems.
We have already covered other types of cooling systems for commercial buildings, supermarket CO2 systems, chillers and chilled water schemes.
Why use ammonia as a coolant?
I just want to explain very briefly why we use ammonia as a coolant.
Ammonia is naturally present in the environment, it is available in abundant quantities. It has an ozone depletion rate of zero and a global warming potential of less than 1. If we compare this with other common refrigerants like R134a with a GWP of 1430, then R404A which has a GWP of 3922, it can see why ammonia is very beneficial to use.
Ammonia is also cheap to produce and energy efficient to use. it has the ability to absorb large amounts of heat as it evaporates. This is a very important aspect for a refrigerant to be useful, it also means that the pipes and components can be thinner and smaller.
However, ammonia is toxic and can also be flammable at certain concentrations. Most refrigerants are odorless, but ammonia has a very sour odor, so it's easy to tell if there's a leak. If ammonia leaks, it will react with carbon and water in the air to form ammonium bicarbonate, which is a harmless washed-out compound.
Single Stage Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System
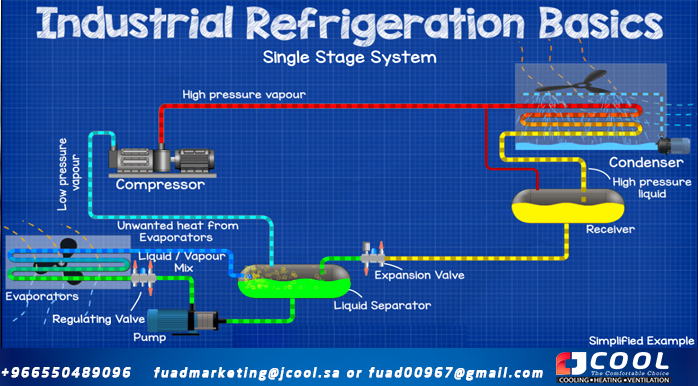 |
| Single Stage Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System |
Single stage, this is the simplest industrial ammonia refrigeration system other than a direct expansion type, so we'll start here
We start with the compressor, it is the heart of the system and is what pumps the ammonia refrigerant around the refrigeration system to provide cooling. It sucks the refrigerant that has collected all the unwanted heat from the evaporator and compresses it into a much smaller volume, so all that heat energy is packed very tightly, making the refrigerant very hot.
The refrigerant enters the compressor as low pressure vapor and leaves as high pressure vapor.
High pressure refrigerant vapor leaves the compressor and flows to the condenser
The condenser cools the refrigerant by removing unwanted heat from the refrigerant and discharging that heat to the outside ambient air. This is usually done by passing hot coolant into a few small tubes and using a fan to force cooler ambient air through the outside of the tubes to cool it down and remove heat. Also, we will often find a small pump spraying water into the pipes, some of it will evaporate and help remove more heat. The refrigerant is sealed inside the pipe and does not come into contact with air or water, it is always separate, the two never meet or mix. Only the heat from the refrigerant passes through the pipe wall and is carried away by the air and water.
When the heat is removed, the refrigerant condenses into a liquid. Therefore, it leaves the condenser as a high-pressure liquid refrigerant and flows into the receiver.
The receiver is a storage container for a tank of liquid refrigerant and holds any unused excess. This allows it to maintain minimal head pressure and also operate under variable cooling loads, providing a damper. We will probably find a line between the receiver and the condenser inlet, this is just to provide pressure equalization and allow liquid refrigerant to flow easily from the condenser to the receiver.
Then the refrigerant flows into the expansion valve that regulates the pressure and the addition of liquid refrigerant to the evaporator circuit.
From the expansion valve, the refrigerant flows into the liquid separator, the liquid flows down and is then usually sucked by a set of refrigerant pumps, these pumps ensure correct circulation through the evaporators when the cooling load varies. . The refrigerant is then pushed to the evaporator expansion valves that regulate the flow of refrigerant to the cooling load.
Cold refrigerant enters the evaporator and passes into tubes inside the evaporator and a fan blows warm room air through the outside of these tubes. The cold refrigerant absorbs this heat, so the air comes out much cooler and makes the space cooler. As the hot air passes through the evaporator tubing, the ammonia boils and evaporates as a part liquid, part vapor mixture. As it evaporates, it evacuates heat. Just like when water boils in a saucepan, steam comes out of the saucepan and carries away the heat. Again, the refrigerant is sealed within the tubing and never comes into contact with or mixes with air, the two are always separate.
The refrigerant leaves the evaporator as a liquid/vapor mixture and returns to the liquid separator. The liquid refrigerant falls and repeats the cycle through the evaporator, and the vapor refrigerant rises and enters the compressor to repeat the entire cycle again. The refrigerant enters the compressor as low pressure vapor refrigerant.
Two Stage Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System
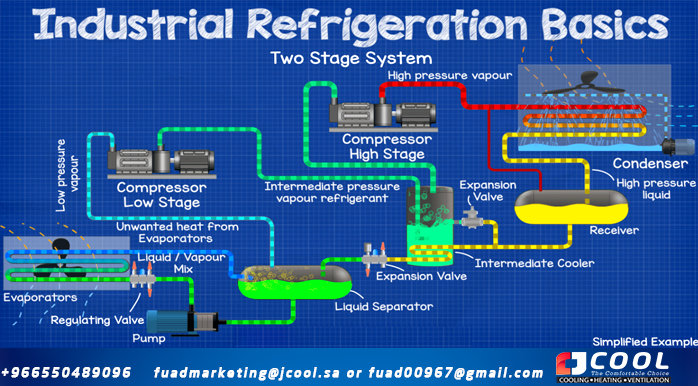 |
| Two Stage Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System |
It is the next evolution of the industrial refrigeration system suitable for low temperature refrigeration systems, providing high efficiency and low compressor discharge temperatures.
We have the refrigerant flowing in the same cycle again, but we have some other components and cycles.
In this type we have a tank called an intercooler that is located between the receiver and the expander. The main flow of refrigerant goes through a coil inside the tank, the refrigerant passes through it and enters the main expansion valve, just like the single stage system, then continues its flow through the separator, the evaporator and returns to the separator. Another flow of refrigerant leaves the main line and is sprayed into the tank through an expansion valve to produce a cooling effect, as spraying and evaporating in the tank cools the submerged coil. This subcools the main flow of refrigerant within the coil before it flows to the main expansion valve.
The refrigerant vapor sucked from the separator still flows to a compressor, but this time we have two compressors, so the refrigerant flows to the low stage or booster compressor to build pressure. From there it flows and is released into the intercooler which helps to condense the coolant.
Refrigerant vapor is drawn from the intercooler and flows to the high stage compressor, where it will then flow back to the condenser to repeat the entire cycle.
Cascade Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System
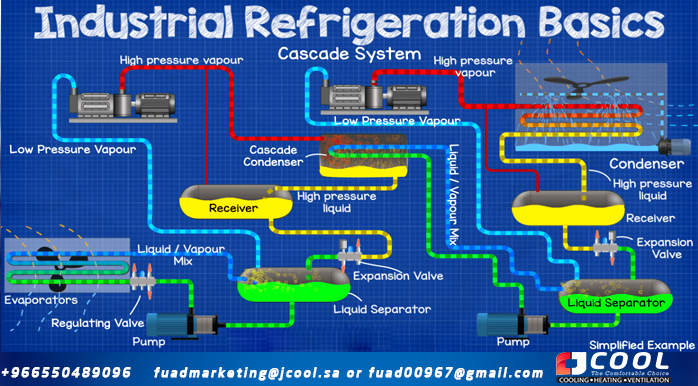 |
| Cascade Ammonia Industrial Refrigeration System |
Cascade this is the most advanced and these systems can become very complex, it is suitable for refrigeration systems that require different temperature ranges for their cooling loads and also makes it easier and cheaper to comply with health, safety regulations and environment.
It's a little daunting when you first look at this system, but if you've been through it all without jumping, you should be able to follow how it works. Just take a moment to trace the pipes and see where it all flows.
These refrigeration systems generally consist of two or more separate refrigeration circuits, often using different refrigerants to provide a cooling effect.
In this system we have two compressors, except that both circulate the refrigerant through separate circuits, a high temperature circuit and a low temperature circuit. Connecting the two circuits is a heat exchanger called a cascade condenser.
This acts as a condenser for the high temperature circuit and as an evaporator for the low temperature circuit.
The two refrigerants can be identical or they can be different and optimized for each circuit. For example, we could use ammonia for the high temperature side and CO2 for the low temperature side.
This would mean less ammonia is used and the system would be more efficient compared to an ammonia only two stage system.
Do you need help maintaining
and repairing an air conditioner?
It's hard to keep cool when the air conditioning
isn't working. Whether it's repairs, air conditioning,
regular maintenance, or assistance with choosing
your new unit, JCOOL professionals can keep
you comfortable all year
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory (JCOOL)
products (condenser coil - evaporator coil -
heat exchanger- air conditioning -
cold evaporator - cooler -industrial air cooler
- tube bundle - air heat exchanger)
Make a reservation immediately with the
maintenance teambefore the summer heat
intensifies.
Let us help you with a lot of maintenance
and installation work on your next project.
To request the service: -
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory
Jeddah - Second Industrial City - Street 49
fuadmarketing@jamjoomarcool.com
fuadmarketing@jcool.sa
Fuad00967@gmail.com
Eng/ Abu Hussam
#heatExchangers #condensers #evaporators
#coolers #coils #airDucts #chiller's #jcool
#Saudi_industry #cooling #ventilation
#radiators #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory
#jamjoom #saudiArabai #coolingtowers #cooling_tower #coolingcoils
#heat_exchanger #heatexchanger #coolingsystems #cooling #chiller
#hvac #jamjoom_hvac #jamjoom_cooling #global_cooling_tower
#Brand_Saudi_Arabia #made_in_Saudi_Arabia #🇸🇦
- TAGS
- #ammonia
- #ammonia_refrigeration
- #ammonia_refrigeration_basics
- #ammonia_refrigeration_system_diagram
- #ammonia_separator
- #ammonia_system
- #animation #
- basics
- #chiller
- #chiller_system
- #compressor
- #condenser
- #cooling
- #cooling_system
- #Cooling_Tower
- #degree #
- engineering_mindset
- #evaporator #
- how_ammonia_system_works
- #HVAC
- #hvac_hacks
- #industrial_engineering #
- industrial_refrigeration #
- learn_hvac
- #pump
- #receiver
- #refrigeration #
- screw_compressor
- #single_stage system
- #two_stage_system
- #working_principle #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory


Comments
Post a Comment