Learn the basics of the different HVAC systems found in typical supermarkets and food retailers.
Scroll down to see the YouTube tutorial.
Learn the basics of the different HVAC systems found in typical supermarkets and food retailers, understand the basics of how they work, and how to integrate them to make the building functional.
🎁 Download the Jamjoomcoil factory eBook for free: HERE
Jamjoomcoil factory solutions help build the supermarkets of tomorrow. With integrated systems and monitoring, supermarkets can reduce costs, minimize environmental impact and gain a competitive advantage, while ensuring food safety. Learn more about Jamjoomcoil factory's smart store solutions in their new e-book, available for free at this link.
Air curtain HVAC systems
The first thing we usually notice when entering a store is the air curtain. It is the breath of air you feel when you enter the building. If it is a large store, we can also find them at the loading docks.
The air curtain hangs over the door or can be integrated into the ceiling. Inside the device is a fan that is driven by a small electric motor, which forces air through a funnel to provide a powerful blast of air. You can also get versions that provide heated and/or cooled air.
Example of an air curtain
This air curtain creates a barrier between the inside and outside air, the two will be at different temperatures and humidity. The store had to pay a lot of money to get the inside air up to a certain temperature and humidity, so we don't want it coming out of the store, and we also don't want too hot or too cold air coming in from outside. store, so these air curtains will greatly reduce the mixing of the two. They also prevent dust, dirt, and insects from entering the tent.
Purpose of the air curtain
Supermarket Main Ventilation
The next thing we notice is the forced ventilation around the tent. In many large supermarkets you will see the ducts for this hanging from the ceiling. The ducts come from air handling units or ceiling units. Both play a very similar role, although rooftop units are more common in supermarkets simply because they are an all-in-one HVAC solution.
Roof Units
As the name suggests, rooftop units are located on the roof of the supermarket and you will usually find multiple units depending on the size of the store. Inside the unit is a large fan that draws cool air into the unit and also pushes it into the building. Some units use this buoyant force to push dirty air out of the building as well. The air passes through a filter to remove dust and dirt, then passes through a heat exchanger where it will be heated or cooled to meet the required conditions.
Rooftop Unit Example
For heating, the roof unit uses an electric resistance, a gas burner or a heat pump.
For cooling, the unit will use either a split air conditioning unit or a heat pump.
For more information on rooftop units, CLICK HERE.
Air treatment units
Air handlers work in much the same way, although they are generally much larger and are usually housed indoors. These units will also filter, heat, cool and humidify the air, although heating and cooling is provided by a remotely connected chiller and boiler. There will also be an extraction CTA to maintain pressure in the building and extract stale air. If the return air is within certain C02, humidity and temperature limits, some of it can be recirculated to reduce the heating or cooling load.
For more information on air handling units, CLICK HERE.
Fan Coils (FCU)
If you look at the ceiling of large stores, you may see a large box connected to a short set of ductwork. This box is a fan coil. Inside the fan coil there is a fan with a small motor, a filter and also one or two heat exchangers. The fan coil simply circulates air locally in the building and supplements the heating or cooling of that local area as needed. They also help diffuse fresh air into the building.
Fan coil units can provide heating and/or cooling and the heat exchangers will be connected to a heat pump, VRF, split air conditioner, chiller or boiler.
For more information on fan coils, CLICK HERE.
fan coil explained
We have covered air handlers, rooftop units and fan coils in detail in our previous articles. Check them HERE.
exhaust ventilation
We are going to generate bad odors in the building in places like restrooms, food preparation areas, and parking lots. This air must be extracted from the building, so these will be connected to dedicated extraction systems. We could find several of these domains connected in a single system or a separate excerpt for each one. There are many different fans, but one of the most common and simple designs is to use a centrifugal type fan like this one. The fan uses a belt-driven motor to spin the fan blades and create a pressure difference, which will draw air in one side and push it out the other.
For staff areas or small businesses we can find a gas boiler system that provides heating through radiators and trench heaters. In the most basic system we find a circulation pump that pushes water through the closed system, collecting the heat from the gas boiler and transmitting it to the radiators. Despite their name, radiators actually dissipate their heat by natural convection, not radiation.
Some stores will also use refrigeration systems to provide space heating and cooling, these will use systems such as VRF, split air conditioning and heat pumps.
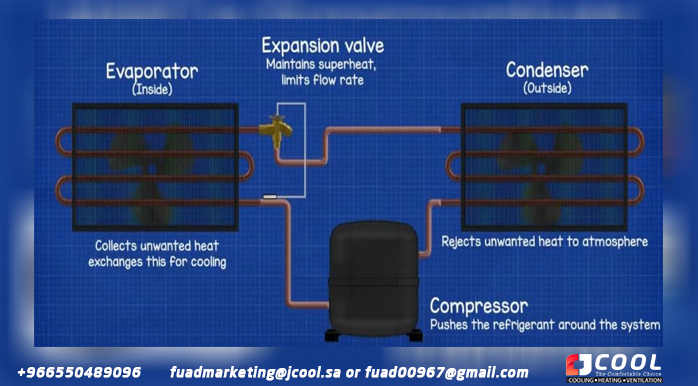
split air conditioner
Split AC is the simplest type; it's just a vapor compression system that uses a compressor, a condenser, an expander, and an evaporator. The compressor pushes refrigerant around the system to collect unwanted heat from the evaporator and deliver it to the condenser. The refrigerant has a very low boiling point, so when it enters the evaporator, the heat in the room will be more than enough for it to boil and evaporate. As the refrigerant evaporates, it builds up unwanted heat and returns it to the compressor. When unwanted heat builds up in the evaporator, it is exchanged for a cooling effect. This type of system will only provide cooling. For more information on split air conditioner CLICK HERE.
Split AC explained
Variable coolant flow system
The next system that we are likely to come across is the VRF or variable refrigerant flow system. This uses a variable speed compressor along with electronic controls and sensors to vary the amount of refrigerant flowing through the system to match the cooling load. This allows the unit to provide cooling to multiple locations simultaneously, although again this version only provides cooling.
Variable coolant flow system
heat pumps
The next variant is the heat pump, which allows the unit to provide cooling or heating, it can alternate between cooling and heating, but can only provide one at a time. It does this by using the reversing valve. This diverts the hot discharge refrigerant from the compressor to the outdoor unit or the indoor unit depending on whether the unit is in heating or cooling mode. There are likely to be multiple expansion valves as well as check valves to ensure the refrigerant is flowing along the correct lines.
In cooling mode, it works as a normal cooling system, recovering heat from the indoor unit and dissipating it to the atmosphere through the outdoor unit.
In heating mode, the system works in reverse, recovering heat from the outside and dissipating it inside. The boiling point of coolant is extremely low, so even outside air in winter can cause it to boil and evaporate. Even when it's cold outside, the air will, in most cases, still contain enough heat energy to boil the refrigerant and thus provide heating.
For more information on heat pumps CLICK HERE.
VRF heat recovery system
Another very common system that we find is the VRF heat recovery system. This uses variable speed compressors along with multiple sensors, valves and electronic controls to provide heating and cooling to different parts of the building.
In cooling mode, the VRF unit works like any AC split unit, absorbing heat from inside and dissipating it through the external outdoor heat exchanger.
VRF heat recovery system
In heating mode, it works like a heat pump, collecting heat energy from the outside ambient air and transferring it to the inside heat exchangers.
In mixed mode, the system can provide cooling in the normal refrigeration cycle, but it can also send heat from the compressor discharge and channel it inside to provide heating. Once the refrigerant has provided heating, it can also flow to another unit to provide cooling.
What about food storage?
Well, you will almost certainly find cold rooms in most supermarkets and these really do vary in size. These use a refrigeration system with an externally located condenser and compressor to extract unwanted heat from food in the storage room and dissipate it to the atmosphere. This diagram shows only a basic system, but many are now equipped with electronically controlled valves, sensors, and speed-controlled compressors to maximize efficiency. For more information on cold rooms CLICK HERE
As for the workshop, we will probably find refrigerators on display. This self-contained type typically has a small, simple vapor compression refrigeration system that is compactly installed below the unit; sometimes the condenser is mounted on the back of the refrigerator and does not use a fan. The regulator may just be a capillary tube on very basic units, but newer and more efficient ones will use electronic controls. This all-in-one, plug-and-play design makes it very easy to move the cooler around the store, but the heat it removes from inside the cooler, as well as the heat from the compressor, is simply vented back into the store. , which will increase the heat load and force the space cooling to work harder.
Large refrigerators are likely to use an external condenser and compressor. This is a better option as it completely removes heat from the cooler and space and then dissipates it to the atmosphere which is more efficient, however the cooler is fixed in place.
What about department stores?
Large stores with aisles of refrigerators and perhaps freezers as well will likely use centralized refrigeration systems. It can be a booster system where the refrigerant is divided between different temperature lines and then the low temperature refrigerant is boosted by a secondary compressor.
It could also be a parallel system using another compressor in parallel to recycle some of the vapor from the receiver. A growing trend is now to use transcritical CO2 refrigeration systems and these will often use a multiple ejector to improve
Transcritical CO2 refrigeration systems
Cascade-type systems can even be found in larger department stores or industrial-scale locations. For more information on industrial refrigeration CLICK HERE
Do you need help maintaining and repairing an air conditioner?
It's hard to keep cool when the
air conditioning isn't working. Whether it's repairs, air conditioning,
regular maintenance, or assistance with choosing your new unit, JCOOL
professionals can keep you comfortable all year
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory (JCOOL) products (condenser coil - evaporator coil - heat exchanger - air
conditioning - cold evaporator - cooler - industrial air cooler - tube bundle -
air heat exchanger)
Make a reservation immediately with the
maintenance team before the summer heat intensifies.
Let us help you with a lot of maintenance and
installation work on your next project.
To request the service: -
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory
Jeddah - Second Industrial City - Street 49
fuadmarketing@jamjoomarcool.com
fuadmarketing@jcool.sa
Fuad00967@gmail.com
Eng/ Abu Hussam
#heatExchangers #condensers #evaporators #coolers #coils #airDucts #chiller's #jcool #Saudi_industry #cooling #ventilation #radiators #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory #jamjoom #saudiArabai #coolingtowers #cooling_tower #coolingcoils #heat_exchanger #heatexchanger #coolingsystems #cooling #chiller #hvac #jamjoom_hvac #jamjoom_cooling #global_cooling_tower #Brand_Saudi_Arabia #made_in_Saudi_Arabia #🇸🇦
- #HVAC#
- AHU System#
- commercial refrigeration#
- Duct System#
- FCU#
- FCU System
- heat pump systems
- heating sys application#
- RTU System
- split ac systems#
- Uncategorised#JCOOL #KSA











Comments
Post a Comment