How do electronic expansion valves work?
 |
| How electronic expansion valves work |
How do electronic expansion valves work? In this article, we'll discuss how electronic expansion valves work, covering the basic principle of operation, where to put them in a refrigeration system, and why you should use them. This covers a simplified version to help you learn the basics of HVAC.
Scroll down to see the YouTube tutorial
Check out these real world electronic regulators, complete technical information and works of art! click here
All HVAC/R systems can benefit from the most complete series of electronic expansion valves on the market. The Danfoss portfolio helps address growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations on CO2 emissions, while delivering significant energy savings and cost reductions.
Learn more here: http://bit.ly/Electronic_expansion_valves
Electronic expansion valves are used in refrigeration systems to precisely control the flow of refrigerant through the evaporator. You can find them in everything, even
· VRF Units
· Inverter mini splits
· heat pumps
· chillers
· AHU batteries
Etc.
We have already explained how thermal expansion valves work, these are very common in refrigeration systems, but they are not as efficient or precise as an electronic expansion valve. If you have not seen the video of how they work, I recommend that you do so by clicking here
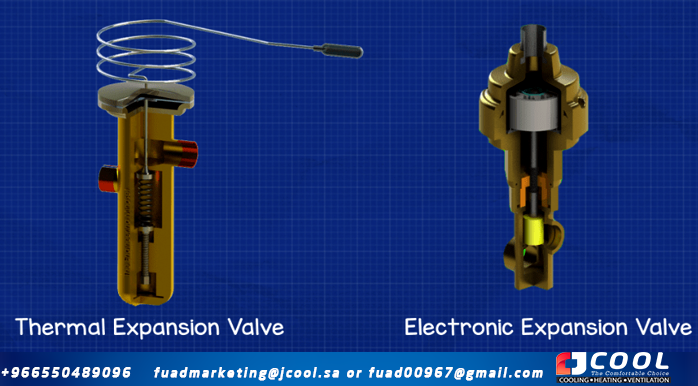 |
| Thermal expansion valve vs electronic expansion valve |
Electronic expansion valves are an evolution of the thermal expansion valve. They are much more sophisticated and allow the cooling system to work much more precisely and efficiently. Typically, you'll see electronic expansion valves listed with the acronym EEV or EXV. They both mean the same thing, it just varies by manufacturer.
Benefits of using an electronic expansion valve
There are many benefits to using an electronic expansion valve and I have listed a few of the main ones on the screen. However, the goal is usually that by using these expansion valves the energy consumption of the refrigeration system is reduced and better performance is achieved.
· precise control
· Fast and accurate response to load change
· Greater part load variation than TXV
· Maintains maximum capacity control even at partial loads
· Injects exactly the right amount of coolant
· Energy savings ~15%
What do electronic expansion valves look like?
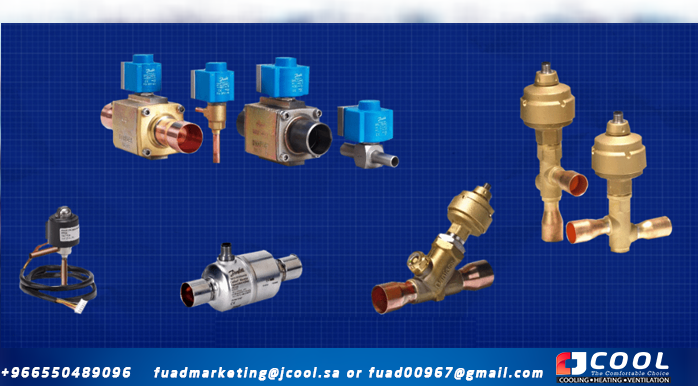 |
| Examples of electronic expansion valves |
There are many different designs for electronic expansion valves, I've put a few examples on screen now so you can see what they look and feel like. The difference in design depends on the type of system, the refrigerant used, and the pressures at which it operates. As you can imagine, a small split air conditioning unit will not need the same valve as a high pressure industrial application, so the design will be different, although the basic principle of operation is basically the same.
Main parts of an electronic expansion valve
As we have just seen, there are many different designs of electronic expansion valves. We will focus on a simplified design to reinforce your basic knowledge. This design uses a permanent magnet stepper motor. In the head of the valve we have the body of the stepper motor which contains the copper coils, these are used to generate an electromagnetic field which will be used to control the position of the valve.
A tree is attached to the permanent magnet. Some designs will use a set of gears between the motor and the shaft, but since we're only looking at a simple design, we'll stick with a direct coupled shaft.
On the shaft there is a thread, this thread is on a bracket that is attached to the valve body. At the end of the shaft is the valve needle. Next we have the valve seat where the needle enters and exits to close and open the valve. And check the coolant flow.
We will also have temperature and pressure sensors to take measurements of the refrigerant to calculate superheating. And these will be connected to a controller. The controller then connects to the stepper motor and will tell it how much to open or close.
How electronic expansion valves work
 |
| Animation of operation of the refrigeration system. |
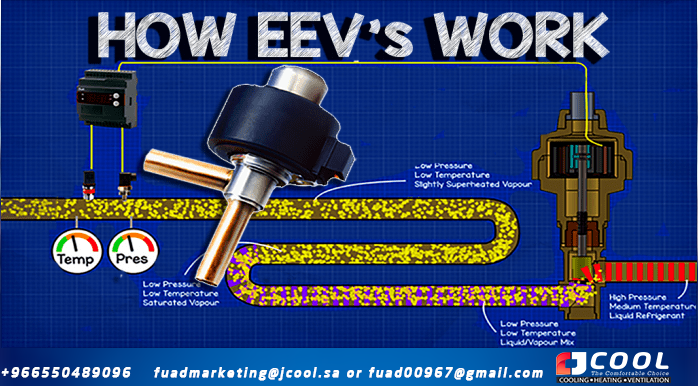
If we look at a refrigeration system, you can see that the main parts are the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. The evaporator collects all the unwanted heat from the building and transfers it to the refrigerant, causing the refrigerant to boil and evaporate.
The compressor sucks in this evaporated refrigerant, which is slightly superheated vapor at low pressure and low temperature, and then compresses it into a smaller volume, turning it into superheated vapor at high pressure and high temperature.
The refrigerant then moves to the condenser where unwanted heat is removed from the refrigerant and released to the atmosphere. This causes the refrigerant to condense into a liquid so that when it leaves the condenser it will be a saturated liquid at high pressure and medium temperature. Then it goes down to the regulator.
The expansion valve creates a pressure difference between the condenser and the evaporator, holds the liquid refrigerant under high pressure and decides how much to go through the evaporator.
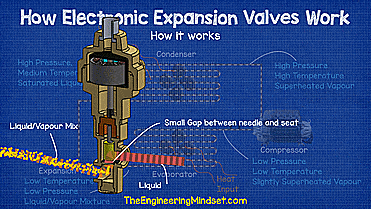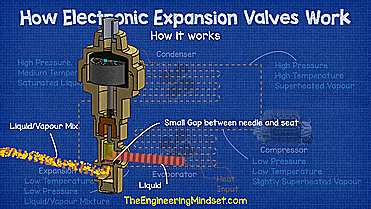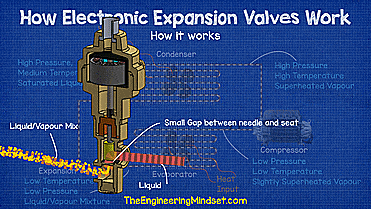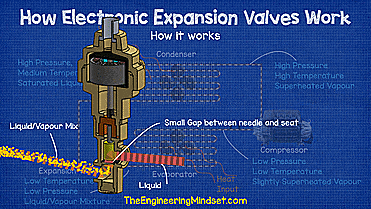 |
| Animation of the operation of an electronic expansion valve |
As the high pressure liquid refrigerant bursts through the small gap between the valve seat and the needle, the pressure will drop, causing some of the refrigerant to vaporize and the rest to remain as a liquid.
If you want to visualize it, it's similar to the spray nozzle on a water bottle, when you pull the trigger, high-pressure liquid is forced through a small hole into a much lower-pressure atmosphere, causing the water to swell. become part liquid and part vapor.
This liquid vapor refrigerant mixture is sprayed into the evaporator where it absorbs heat from the air or water surrounding the outside of the tubing that forms the evaporator coil, in this case a fan blows from the air through the evaporator coil. evaporator.
As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator coil, it is exposed to thermal energy that will cause it to undergo a complete phase change from liquid to saturated vapor, always at low pressure and temperature. During this change, there will be little or no change in temperature due to latent heat, and instead entropy and enthalpy will increase. Since heat energy is still applied to the steam towards the evaporator outlet, there is no more liquid to turn into a gas, so the refrigerant will rise in temperature and superheat.
 |
| Operation of an electronic expansion valve - principle of operation |
After the evaporator we will find a pressure transducer and a temperature sensor that constantly take measurements and send this data to the controller. Not all electronic expansion valves will use this method, it depends on the manufacturer and the system, some simple ones will use a single thermistor at the evaporator outlet, some will use two thermistors one at the inlet and one at the outlet and then use differential temperature as superheat , but in this example we were going to focus on the pressure and temperature method because it is a very reliable method and you are likely to encounter it in the real world.
The controller measures and converts the pressure, using the data stored for the refrigerant used in the system to find the saturation temperature, this is then compared to the actual temperature measurement, the difference between the two being the operating superheat. The controller then decides whether the expansion valve should open to allow more refrigerant to enter the evaporator or close to reduce the amount entering the evaporator.
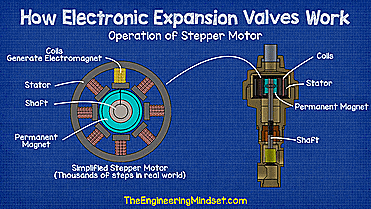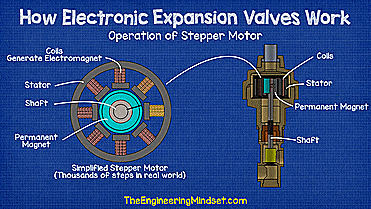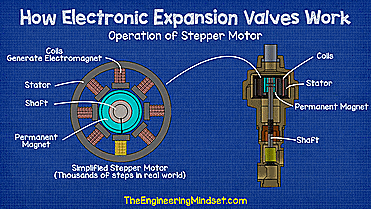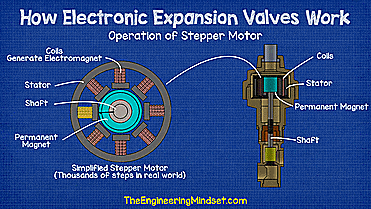 |
| How a stepper motor works - working animation |
Once decided, the controller sends electrical signals to the expanders stepper motor to energize the coils and create an electromagnetic field and vary its polarity, this forces the permanent magnet to rotate clockwise or counterclockwise depending on the generated polarity. Each time a signal is sent, the permanent magnet rotates a fraction of a turn to provide very precise superheat settings.
The shaft that is connected to the permanent magnet will also rotate, and as it does, the threaded section inside the bracket will lower the assembly. As the assembly is pulled down, the valve needle reaches the seat, reducing the gap between the two and restricting the flow of coolant.
When the signal to open the valve is sent, the assembly rotates in the opposite direction and the threaded section pulls the assembly up, this opens the valve and moves the needle away from the seat allowing more refrigerant to flow. The controller constantly takes pressure and temperature measurements and sends signals to adjust the valve position according to the load.
As the cooling load increases, the refrigerant in the evaporator will evaporate much faster and the suction line pressure and temperature increase, the expansion valve senses this and opens to let more refrigerant in.
As the cooling load decreases, the refrigerant evaporates more slowly, and the suction line pressure and temperature decrease, the expansion valve begins to close to allow less refrigerant to enter the evaporator and maintain the correct superheat.
Do you need help maintaining
and repairing an air conditioner?
It's hard to keep cool when the air conditioning
isn't working. Whether it's repairs, air conditioning,
regular maintenance, or assistance with choosing
your new unit, JCOOL professionals can keep
you comfortable all year
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory (JCOOL)
products (condenser coil - evaporator coil -
heat exchanger- air conditioning -
cold evaporator - cooler -industrial air cooler
- tube bundle - air heat exchanger)
Make a reservation immediately with the
maintenance teambefore the summer heat
intensifies.
Let us help you with a lot of maintenance
and installation work on your next project.
To request the service: -
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory
Jeddah - Second Industrial City - Street 49
fuadmarketing@jamjoomarcool.com
fuadmarketing@jcool.sa
Fuad00967@gmail.com
Eng/ Abu Hussam
#heatExchangers #condensers #evaporators
#coolers #coils #airDucts #chiller's #jcool
#Saudi_industry #cooling #ventilation
#radiators #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory
#jamjoom #saudiArabai #coolingtowers #cooling_tower #coolingcoils
#heat_exchanger #heatexchanger #coolingsystems #cooling #chiller
#hvac #jamjoom_hvac #jamjoom_cooling #global_cooling_tower
#Brand_Saudi_Arabia #made_in_Saudi_Arabia #🇸🇦
- TAGS
- #ahu
- #air_conditioning
- #air_handling_unit
- #animated_expansion_valve
- #Central_Plant
- #chilled_water
- #chiller
- #compressor
- #cooling_load
- #jcool
- #EEV
- #electronic_expansion_valve
- e #xpansion_valve
- #EXV
- #heat_pump
- #how_does_an_electronic_expansion_valve_work
- #hvac_basics
- #HVAC_Classes #
- hvac_hacks
- #hvac_meaning
- #HVAC_School
- #HVAC_Training #
- hvac_training_videos #
- HVACR
- #Online_HVAC_Classes
- #Online_HVAC_Training
- #refrigeration
- #thermal_expansion_valve
- #thermostatic_expansion_valve
- #txv
- #vrf
- #vrv #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory



Comments
Post a Comment