How thermostatic expansion valves work
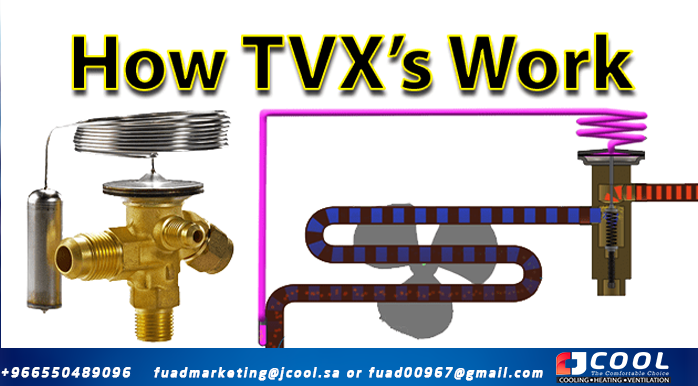 |
| How thermostatic expansion valves work |
In this article, we will learn how thermostatic expansion valves work. The expansion valve is an essential component in almost all refrigeration cycles and the thermostatic expansion valve is most commonly used in HVAC systems.
If you are in the HVAC industry and need high quality Thermostatic Expansion Valves for your refrigeration system, I highly recommend checking out what jcool has to
offer. Its product line is universal and adaptable, offering exceptional quality and reliability, as well as a wide range of capacities and refrigerants. You can learn more about Jcool's Thermostatic Expansion Valves by visiting TXV.Danfoss.com
Naming convention.
The correct name for this type of valve is a thermostatic expansion valve, however it is often abbreviated to thermal expansion valve and has the acronym TXV or sometimes TEV.
Where can I find the thermostatic expansion valve?
The TXV is used in many refrigeration systems, from simple split units to chillers. Small refrigeration units, such as domestic refrigerators, would not normally use a valve and would instead use a fixed orifice capillary. No matter what type of expansion device is used, they can all be found in the same place, just before the evaporator.
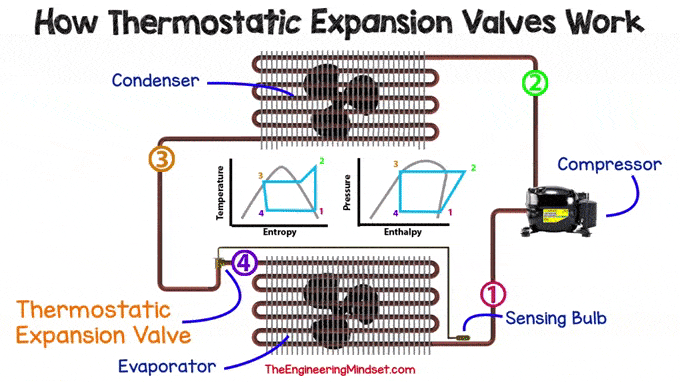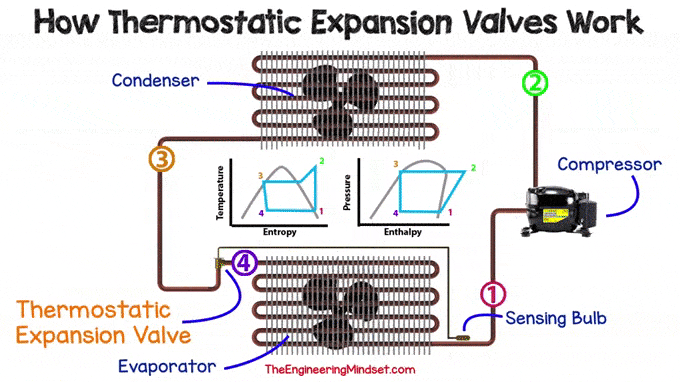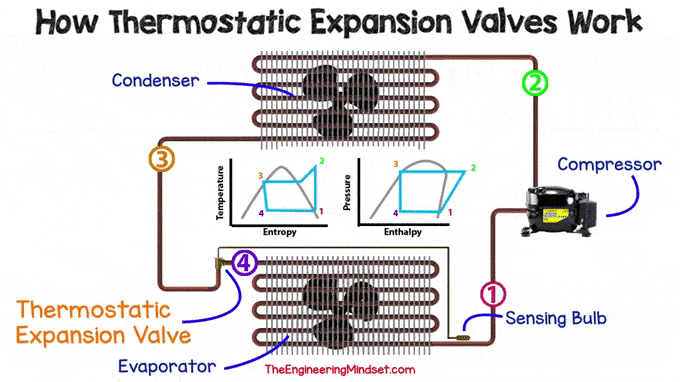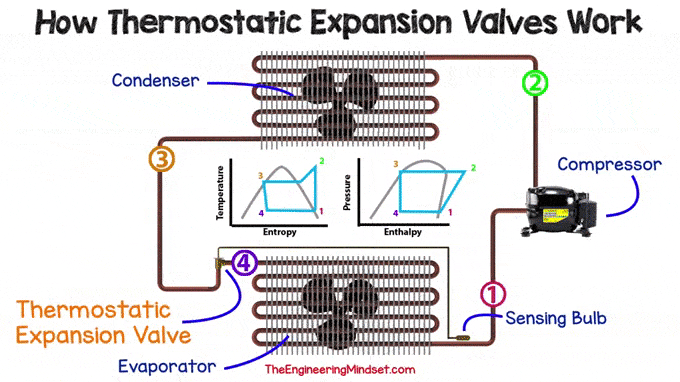 |
| Location of TXV in the cooling system |
Main components
There are many design variations for this type of valve, but they all follow the same basic principle of operation.
Inside the regulator, you will typically find the following major components
· The valve body, this contains the components and has an orifice inside it to limit the flow of refrigerant.
· The diaphragm, which is a strong, thin flexible material, usually metal, that can flex to apply pressure to the pin.
· The pin, or needle, that moves up and down to vary the size of the opening in the hole to control the flow of coolant.
· The spring that counteracts the force of the pin.
· The sensing bulb and capillary line that senses the temperature of the refrigerant leaving the evaporator and reacts to cause the valve to open or close.
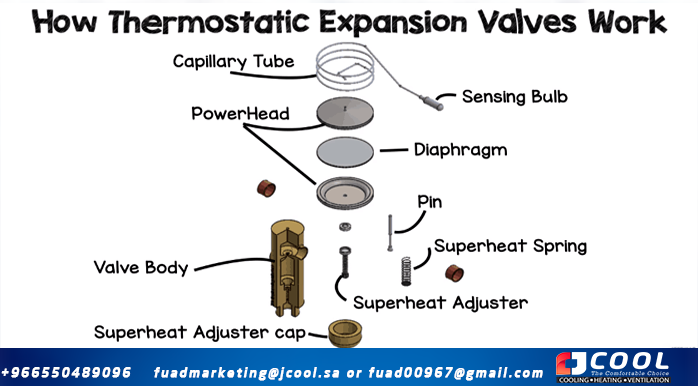 |
| Main components of the thermostatic expansion valve |
How does it work?
The valve retains high pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser and controls the amount of refrigerant that can pass through the evaporator.
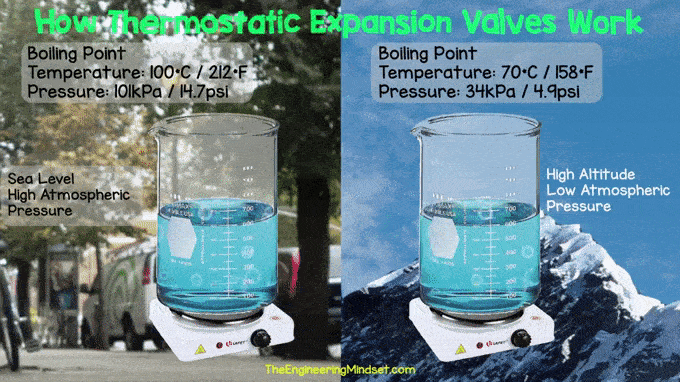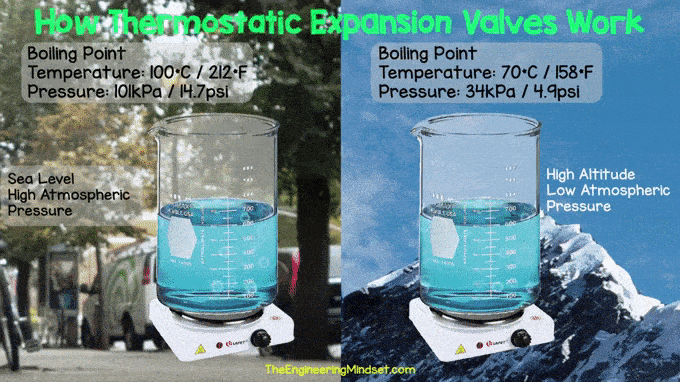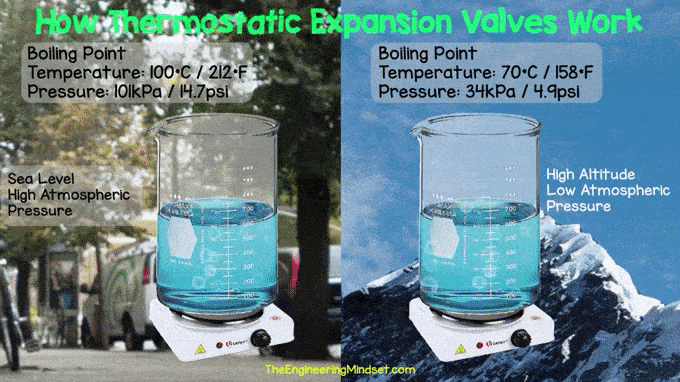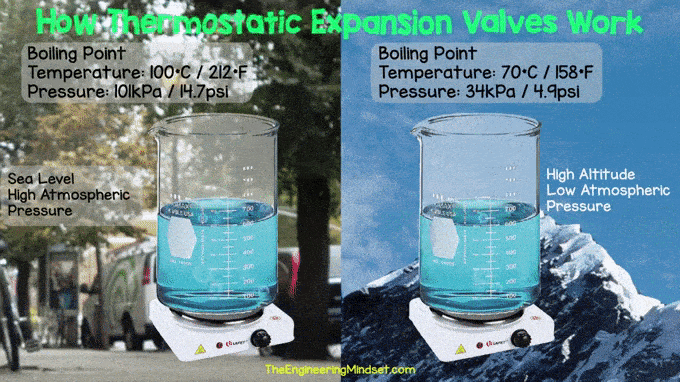 |
| boiling water at sea level and at high altitudes |
The valve reduces the pressure to allow the refrigerant to boil at lower temperatures. For example, we are used to water boiling at around 100 °C (212 °F) because most of us live near sea level, so the air around us is compressed by the full weight of the atmosphere that is above us. However, if we were to go higher in the atmosphere, say to the top of Mount Everest, we would find that water boils at only 158 °F (70 °C) and that is because we are higher up so there is less atmosphere. . above us to push the water, making it boil more easily. Boiling is essential because the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surrounding air and carries it to the compressor. Remember that refrigerants have a much lower boiling point than water. If you want to learn more about how coolants work, you can read or watch our
tutorial here.
High pressure liquid refrigerant is forced through a small orifice causing a drop in pressure as it passes through. During this pressure reduction, part of the refrigerant will vaporize and the rest will remain in liquid form. Similar to the spray nozzle on a water bottle, when you pull the trigger, high-pressure water is forced through the small hole into a much lower-pressure environment. This causes the water to become part liquid and part vapor.
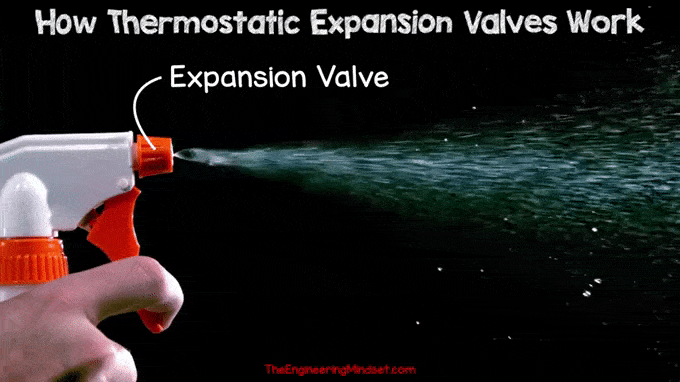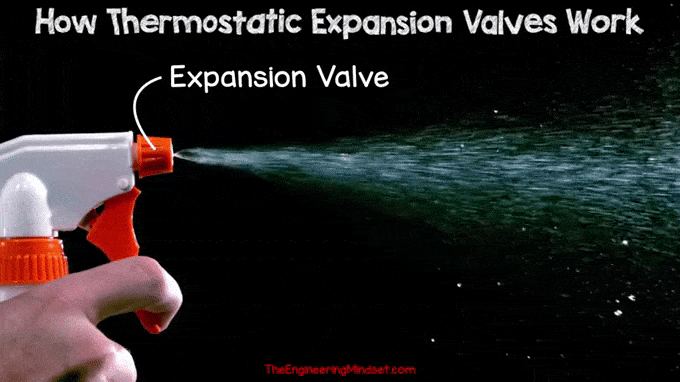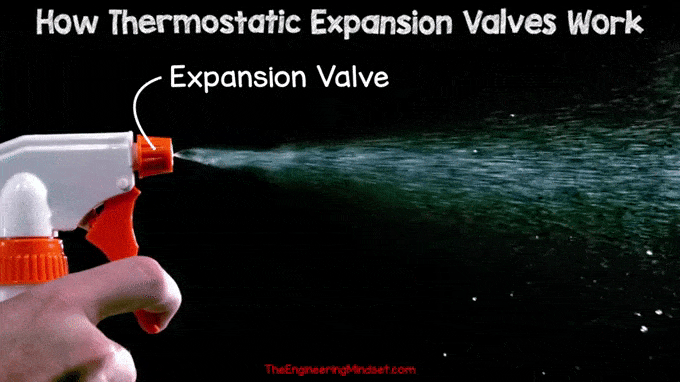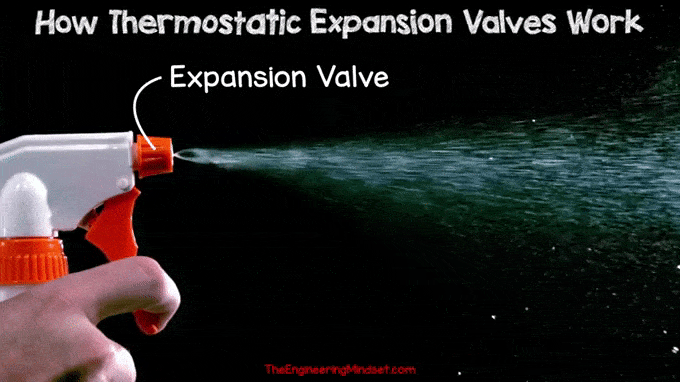 |
| Spray Tip Regulator |
This liquid/vapor refrigerant mixture is sprayed into the evaporator, where it will absorb heat from the air or water surrounding the pipe. In this example, a fan blows air across the evaporator.
 |
| Thermostatic Expansion Valve Animation |
As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator and is exposed to more heat energy, it will undergo a complete phase change and become saturated vapor towards the end of the evaporator coil. During this change, there will be little to no temperature change due to latent heat. Instead, it will increase in enthalpy and entropy.
The refrigerant will continue to accumulate thermal energy and when it does after the phase change, its temperature will begin to increase. This superheats the refrigerant vapor. The expansion valve sensing bulb monitors this temperature to control the refrigerant in the main valve body.
Increase heat load, thermostatic expansion valve
If the refrigeration load increases, more refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator. This will lead to an increase in superheat, which means that the temperature of the refrigerant will rise at the outlet of the evaporator.
The superheat temperature should remain within expected limits. So now it must decrease and this can be achieved by allowing more refrigerant to flow to the evaporator. Therefore, the pin must be depressed to compress the spring and allow more coolant to flow through the hole in the main valve body.
Inside the sensing bulb is a small amount of coolant that is separated from the rest of the system and is limited, in a closed system, only to the volume inside the bulb, capillary tube, and drive head
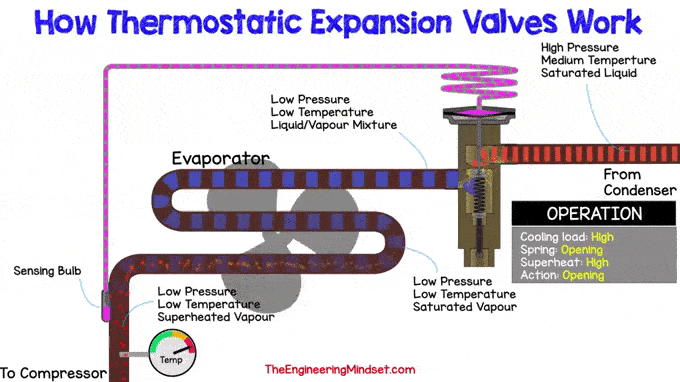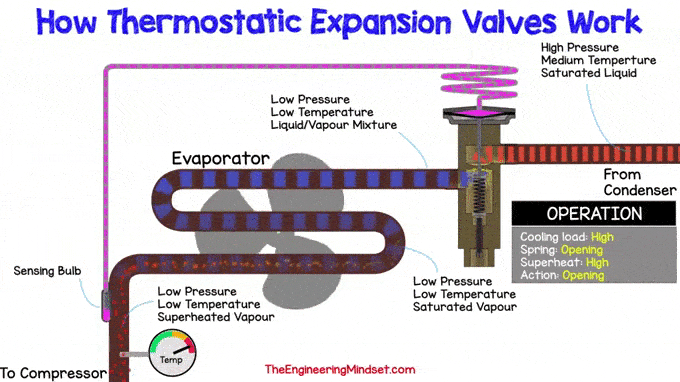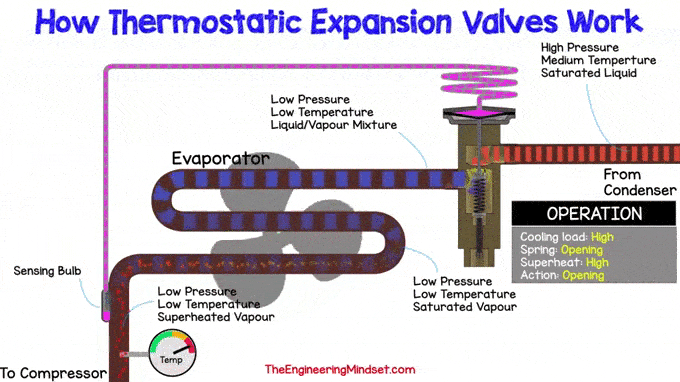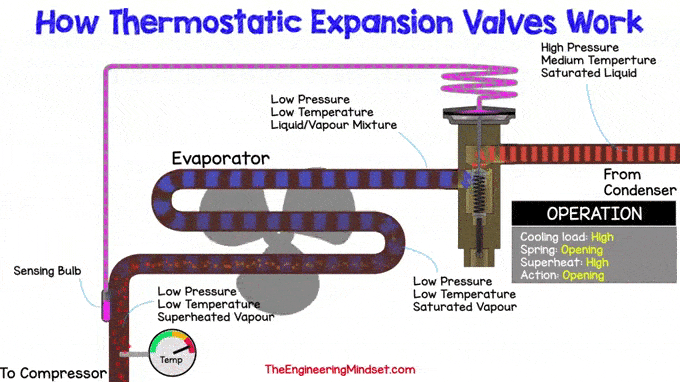 |
| Increase heat load, thermostatic expansion valve |
The sensing bulb senses the rise in temperature as heat energy is transferred through the pipe wall into the bulb. This heat energy causes the refrigerant inside the bulb to boil and evaporate. Since the refrigerant is restricted to a small area, this will cause pressure to build up, pushing up the length of the capillary tube and onto the top of the expansion valve. This pushes down on the diaphragm, which pushes down on the pin that compresses the spring and allows more refrigerant into the evaporator.
The valve will adjust to find the correct position so that the force on the diaphragm is greater than or equal to the force of the spring pushing in the opposite direction. This allows the correct amount of coolant through which the superheated coolant temperature decreases, the sense bulb detects this and adjusts until equal.
Reduced cooling load
If the cooling load returns to normal, the superheat temperature will drop. The sensing bulb will detect this and begin to reduce the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator. Then the refrigerant in the capillary returns to the bulb and the main valve begins to close. The superheat temperature will also start to rise when this happens.
Eventually the valve will balance itself and the correct amount of refrigerant will flow to match the superheat setting.
This all happens automatically using this type of valve, which is why it is so popular. There are other electronic expansion versions of this valve that provide greater precision, but more on that in a later article.
Valve failure or incorrect superheat setting
If the valve didn't respond to overheating, it could let liquid refrigerant pass right through the compressor. Compressors hate this because liquids can't be easily compressed. If liquid gets into the compressor, it can cause internal damage.
Do you need help maintaining
and repairing an air conditioner?
It's hard to keep cool when the air conditioning
isn't working. Whether it's repairs, air conditioning,
regular maintenance, or assistance with choosing
your new unit, JCOOL professionals can keep
you comfortable all year
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory (JCOOL)
products (condenser coil - evaporator coil -
heat exchanger- air conditioning -
cold evaporator - cooler -industrial air cooler
- tube bundle - air heat exchanger)
Make a reservation immediately with the
maintenance teambefore the summer heat
intensifies.
Let us help you with a lot of maintenance
and installation work on your next project.
To request the service: -
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory
Jeddah - Second Industrial City - Street 49
fuadmarketing@jamjoomarcool.com
fuadmarketing@jcool.sa
Fuad00967@gmail.com
Eng/ Abu Hussam
#heatExchangers #condensers #evaporators
#coolers #coils #airDucts #chiller's #jcool
#Saudi_industry #cooling #ventilation
#radiators #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory
#jamjoom #saudiArabai #coolingtowers #cooling_tower #coolingcoils
#heat_exchanger #heatexchanger #coolingsystems #cooling #chiller
#hvac #jamjoom_hvac #jamjoom_cooling #global_cooling_tower
#Brand_Saudi_Arabia #made_in_Saudi_Arabia #🇸🇦
- TAGS
- #a/c
- #jcool #
- expansion
- #expansion_valve
- #HVAC #
- HVAC_School
- #HVAC_Training
- #refrigerant #
- refrigerants
- #tev
- #Thermal #
- thermal_expansion_valve
- #thermostatic
- #thermostatic_expansion_valve
- #txv
- #valve #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory


Comments
Post a Comment