The essential knowlege of refrigeration
A fluid, called a refrigerant, moves between four key stages of the refrigeration cycle. As it does so, it changes the pressure and temperature, allowing the fluid to absorb heat from one place and discharge it to another.
For a refrigeration cycle to work, five main components are required. The four key stages of temperature and pressure change occur within these components.
- Tthe compressor
- the condenser
- the regulator
- the evaporator
- The pipeline that connects them all.
 |
| Animation of the refrigeration cycle |
1. Compressor
To cool a room, you have to capture the heat and reject it elsewhere. The air in that "elsewhere" must be at a lower temperature than the coolant in order for you to dissipate the heat. To ensure this is possible, the coolant is compressed so that the temperature rises. This way, when the refrigerant reaches the condenser, the refrigerant inside the pipe will be hotter than the air outside the pipe, so it can carry the heat away. If the pipe were at the same temperature as the air, you wouldn't be able to reject the heat and you wouldn't cool the room.
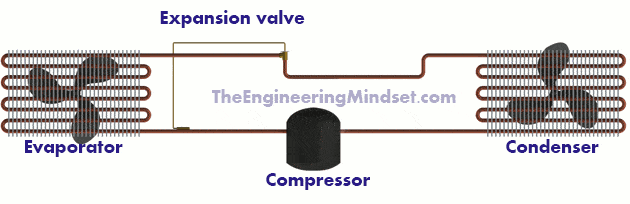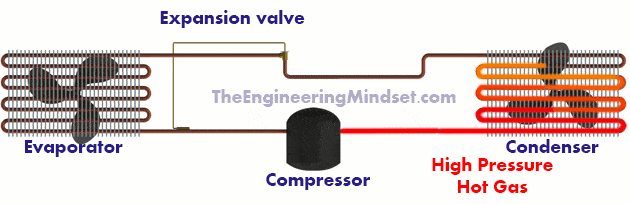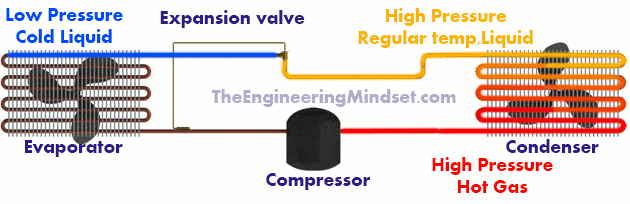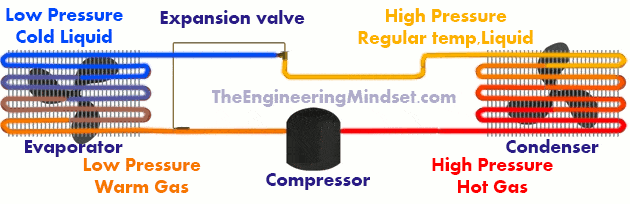
The refrigerant enters the compressor as a hot saturated gas at low pressure, then it is compressed in the compressor (hence its name). During compression, the amount of fluid stays the same but the volume decreases, this increases the pressure and temperature. The refrigerant leaves the compressor as a superheated (hot) high-pressure gas.
 |
| Compressor |
2. Condenser
This superheated high pressure gas then enters the condenser, the condenser is a coil of tubing that passes between metal fins.
Metal fins help draw heat away from the pipe. A fan also blows air through the coil and fins to remove heat by convection.
As air is blown through the pipes and fins, it takes heat from the refrigerant and carries it away to cool the refrigerant. As it cools, the high-pressure gas condenses into a liquid, which is still under high pressure.
The refrigerant enters the condenser as a superheated (hot) high-pressure gas, it pours its heat into the air blown by the fan, this drop in temperature condenses the refrigerant. The refrigerant leaves the condenser as a saturated liquid under high pressure at a regular temperature.
.gif) |
| Condenser |
3. Regulator
In order to cool a room, the heat within that room must be collected and evacuated elsewhere. The refrigeration cycle collects this heat by sending the refrigerant at low temperature and pressure through the evaporator in this room.
To cool the refrigerant it is passed through the expansion valve, this will reduce the pressure of the refrigerant by limiting the amount that can flow through the valve. This restriction means that there will be less refrigerant in the next section of pipe, so the refrigerant that is let through can expand a bit. This expansion reduces the temperature and gives you a storage space to collect heat.
The expansion valve limits the flow of refrigerant through the use of an internal spring-loaded valve that is connected to a diaphragm.
A thin tube, called a capillary tube, runs between the expansion valve and a heat bulb. The heat bulb is in contact with the pipe just after the evaporator, the liquid/vapor inside the heat bulb expands and contracts with the change in temperature of the refrigerant leaving the evaporator. This expansion and contraction causes the diaphragm to move, which in turn controls the spring-loaded valve that limits the flow of refrigerant to the evaporator.
The refrigerant enters the expansion valve as a saturated liquid under high pressure at a uniform temperature. The expansion valve will limit the amount of refrigerant that can pass at one time, causing a drop in refrigerant pressure and temperature. The refrigerant leaves the expansion valve as a cold, saturated liquid at low pressure.
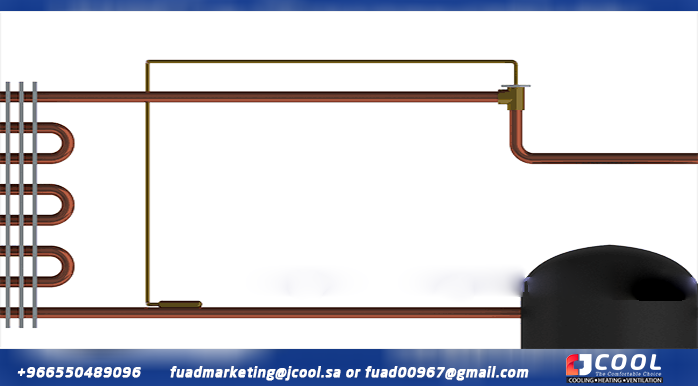 |
| Expansion valve |
The last key step in the refrigeration cycle is the component called the evaporator. This is similar to the condenser under construction, but the refrigerant behaves differently inside.
In the evaporator, the refrigerant enters as a cold liquid at low pressure but quickly begins to boil. Coolant has a very low boiling point, typically -23ºC (minus twenty-three degrees Celsius). When the refrigerant boils it evaporates, this evaporation captures the heat from the room and takes it to the compressor where the refrigeration cycle will start again.
The refrigerant enters the evaporator as a cold liquid under low pressure, the refrigerant begins to boil and evaporate, this evaporation causes a cooling effect in the room, and the heat is removed to be discharged into the condenser after the compressor. The refrigerant leaves the evaporator as a hot saturated gas at low pressure.
.gif) |
| Evaporator |
Do you need help maintaining and repairing an air conditioner?
It's hard to keep cool when the air conditioning isn't working. Whether it's repairs, air conditioning, regular maintenance, or assistance with choosing your new unit, JCOOL professionals can keep you comfortable all year
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory (JCOOL) products (condenser coil - evaporator coil - heat exchanger - air conditioning - cold evaporator - cooler - industrial air cooler - tube bundle - air heat exchanger)
Make a reservation immediately with the maintenance team before the summer heat intensifies.
Let us help you with a lot of maintenance and installation work on your next project.
To request the service: -
Jamjoom Cooling Systems Factory
Jeddah - Second Industrial City - Street 49
WhatsApp +966 550 489 096
fuadmarketing@jamjoomarcool.com
fuadmarketing@jcool.sa
Fuad00967@gmail.com
Eng/ Abu Hussam
#heatExchangers #condensers #evaporators #coolers #coils #airDucts #chiller's #jcool #Saudi_industry #cooling #ventilation #radiators #jcool #jamjoomCoil #jamjoom_cooling_systems_factory #jamjoom #saudiArabai #coolingtowers #cooling_tower #coolingcoils #heat_exchanger #heatexchanger #coolingsystems #cooling #chiller #hvac #jamjoom_hvac #jamjoom_cooling #global_cooling_tower #Brand_Saudi_Arabia #made_in_Saudi_Arabia #🇸🇦
- TAGS
- #a/c
- #air_conditioning
- #compressor
- #condenser
- #engineering
- #evaporator
- #expansion_valve
- #gas
- #r134a
- #refrigerant
- _refrigeration_cycle



Comments
Post a Comment